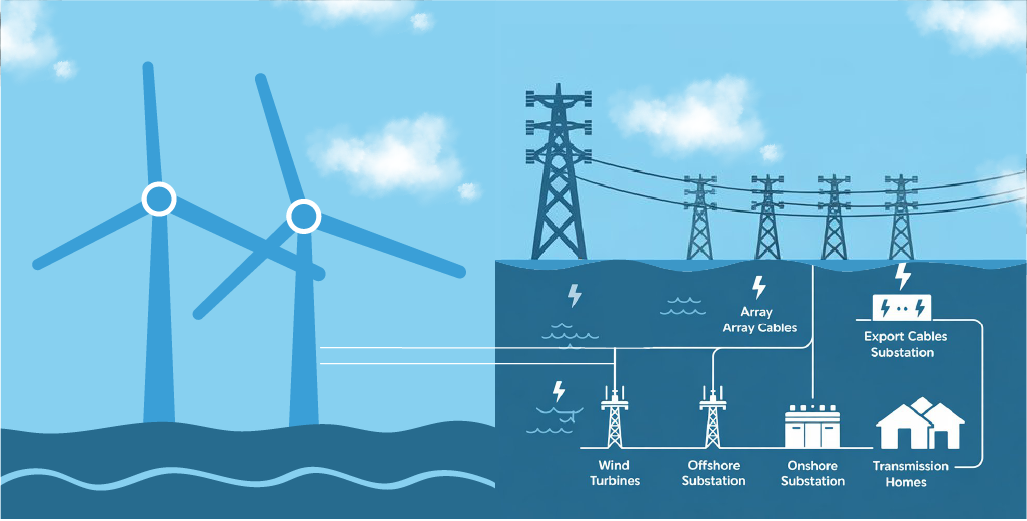
What is Wind Energy?
By using turbines, wind’s kinetic energy is turned into usable power, helping reduce our dependence on fossil fuels and cutting harmful greenhouse gas emissions.
This eco-friendly solution works for both large wind farms and smaller home systems. Wind energy is widely available, cost-effective in the long run, and an important step toward green energy. Whether you’re thinking about renewable power for your home or just curious about sustainable technology, learning the basics of wind energy can help you make smarter choices for a cleaner future.